[上課] Modern React with Redux - 學習筆記
關於筆記
這個學習筆記是我觀看Udemy的線上課程「Modern React with Redux」的過程中所記錄下來的。
這個影片我沒有看完,所以筆記不包含影片的所有內容,不過主要內容應該還是含概了很大一部份的基本知識;我影片大約看到了 Hooks為止,更後面的 Router、Redux(狀態管理套件)、以及實作的部份我就沒有看了。
因為是當時的學習筆記,格式比較 free style… 懶得做修飾了請見諒 XD
第1節:Let's Dive In!
hello world練習
https://codesandbox.io/s/react-yud4c?file=/src/App.js
create react app
https://create-react-app.dev/docs/getting-started/#quick-start
安裝create react app
npm install -g create-react-app
建立專案
npx create-react-app my-app
程式碼比較
第 2 節: Building Content with JSX
可以線上測試將 JSX即時轉換為 js
HTML to JSX 使用Codepen
差異:
HTML
<div style="background-color:white"></div>
JSX
<div style={{backgroundColor: 'white'}}></div>
雙花括號第一個括號是宣告變數區塊、第二個括號是物件
class是 js的保留字,所以 JSX裡內用 className來取代(實際上不是真的會造成保留字的衝突,只是開發者當初在設計時想避免 coding時混肴、以及預防在不同開發工具上造成無法預期的錯誤)
for => htmlFor 取名原因同 className
第 3 節: Communicating with Props
課程範例採用的UI框架 https://semantic-ui.com/
三個 Component的強項:Nesting、Reusability、Configuration
產生假資料
https://github.com/marak/Faker.js/
巢狀Component中,子Component會作為props傳入父Component(概念類似於Vue的slot)
父Component引入子Componet在 JSX中的寫法:{props.children}
第4節:Structuring Apps with Class-Based Components
相較於Classed Component,Function Component天生較受限制 (restricted),沒有 lifecycle method系統和 state系統,現今使用 hooks system來操作 lifecycle 和 state
function component 不能自動 rerender或暫停render動作(不能用非同步的方式取得資料來做render)
第5節:State in React Components
課程中用 html原生的 geolocation api(window.navigator.gelocation.getCurrentPosition())來示範非同步程式,這個範例還蠻不錯的
State is a javascript object that contains some amount of data that is relevant to a singular component
用更新state的方式來rerender component
只能用setState function來更新 state,不能直接對 state賦值。唯一的例外是在 constructor中初始化 state的時候才會直接賦值
setState 只能「新增」或「修改」state,不能「移除」state
Component必要的methods:
class App extends React.Component {
constructor (props) {
super(props) // constructor可省略,但有寫的話必須要有super(繼承),並將props傳入super
}
// 必須宣告render否則會出錯
render () {
}
}
第6節:Understanding Lifecycle Methods
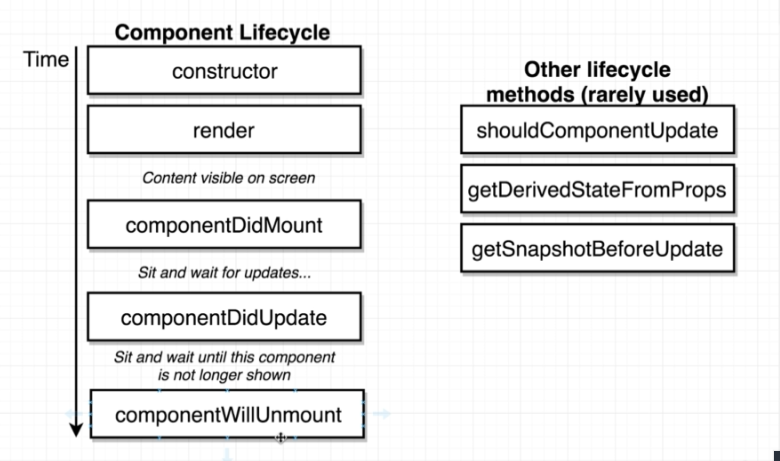
初始化渲染時的執行順序 render() -> componentDidMount()
初始化完成之後每次重新渲染的執行順序 render() -> componentDidUpdate()
建議不要在 constructor裡做取得 api資料(互非同步取資料)的動作,最好在 componentDidMount裡做,理由是讓 code比較簡潔
初始化 state的兩種寫法:
class App Extends React.Component {
contructor (props) {
super(props)
// 第一種寫法
this.state = { lat: null, errorMessage: '' }
}
// 第二種寫法(影片說會經由babel編譯,不曉得這個是不是es6原生的語法?)
state = { lat: null, errorMessage: '' }
}
講者習慣將 component最外層元素加上和 component相同名稱的 css class name
兩種設定 props預設值的方法
const Spinner = (props) => {
return (
// 略
{props.message || 'Loading..'} // 第一種方法
)
}
// 第二種方法
Spinner.defaultProps = {
message: 'Loading..'
}
講者建議不要在 render function內寫多個 return
render function的 JSX可以抽出來寫成回傳 JSX的 function
renderContent () {
if (this.state.lat) {
return <SeasonDisplay />
} else {
return <Spinner />
}
}
render () {
return {this.renderContent()}
}
第7節:Handling User Input With Forms and Events
事件properties:onClick, onChange, onSubmit...
onInputChange (event) {
console.log(event.target.value)
}
render () {
return (
<input
type="text"
onChange={this.onInputChange}
onClick={(event) => console.log(event.target.value)}
/>
)
}
Controlled vs Uncontrolled Element
以下例子說明什麼是 Controlled Element(我的理解以這個例子等同於Vue的雙向綁定)
state = { term: '' }
render () {
return (
<input
type="text"
value={this.state.term}
onChange={e => this.setState({ term: e.target.value })}
/>
)
}
Controlled Element: value存放在 state
Uncontrolled Element: value存放在 dom裡面,必須要從 dom取出來後才能知道 value是什麼
我們應該將所有資訊存放在 Component內
this會指向到呼叫 (call) 該 function(或method)的對象身上,所以事件調用的 callback function中的 this會跑掉,找不到 component,如下範例
state = { term: '' }
onFormSubmit (event) {
console.log(this.state.term) // 'this' undefined
}
render () {
return (
<form onSubmit={this.onFormSubmit} >
(略)
)
}
*第 90集的範例說明的蠻清楚的
解決方式1
constructor () {
this.onFormSubmit.bind(this)
}
解決方式2(箭頭函式會自動綁定this到 function所在的物件上)
onFormSubmit = (event) => {
console.log(this.state.term) // 'this' undefined
}
解決方式3 - callback函式用箭頭函式再回傳一次(有點特別@@)
render () {
return (
<form onSubmit={e => this.onFormSubmit()} >
(略)
)
}
子傳父的溝通方式:調用父 Component傳入的 callback function(做的事情等同Vue的 emit)
測試 js輸出結果的網頁
https://stephengrider.github.io/playgrounds/
第8節:Making API Requests with React
測試用的免費api
第9節:Building Lists of Records
跑迴圈做渲染的時候需要有一個 key property給 react作為索引
const ImageList = props => {
const images = props.images.map({ description, id, url} => {
return <img alt={description} key={id} src={urls.regular} />
})
return <div>{images}</div>
}
第10節:Using Ref's for DOM Access
這個章節介紹用 CSS Grid方法結合 react ref來製作瀑布式圖片列表,還蠻有趣的,有時間可以練習看看。但我覺得最後成果的高度間隔微小的不一致看起來還是有點不太順眼,不曉得有沒有更好的解法
componentDidMount 雖然已將 dom渲染上去,但圖片的渲染還沒真正完成
constructor (props) {
super(props)
this.state = { spans: 0 }
this.imageRef = React.createRef()
}
componentDidMount () {
this.imageRef.current.addEventListener('load', this.setSpans)
}
setSpans = () => {
const height = this.imageRef.current.clientHeight
const spans = Math.ceil(height / 10)
this.setState({ spans })
}
render () {
const { description, urls } = this.props.image
return (
<div style={{ gridRowEnd: `span ${this.state.spans}` }}>
<img ref={this.imageRef} alt={description} src={urls.regular} />
</div>
)
}
第12節:Understanding Hooks in React
React.Fragments 是一個可以不渲染出元素的標籤
render() {
return (
<React.Fragment>
<ChildA />
<ChildB />
<ChildC />
</React.Fragment>
);
}
callback function要傳入參數時的寫法如下
// 會立刻被執行
<div onClick={onTitleClick(index)}>
// 用箭頭函式改寫成callback
<div onClick={() => onTitleClick(index)}>
setState 寫法
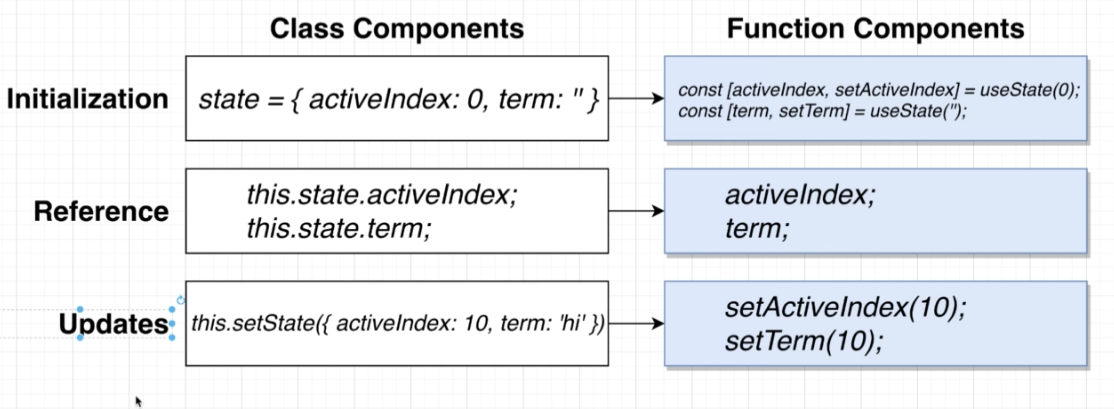
import React, { useState } from 'react'
// const [<state>, <setter>] = useState(<default>)
const [activeIndex, setActiveIndex] = useState(null)
Wikipedia API
en.wikipedia.org/w/api.php?action=query&list=search&format=json&srsearch=SEARCHTERM
useEffect 我的理解他的功能就等同 Vue的 watch,第二個參數就是他監聽的對象
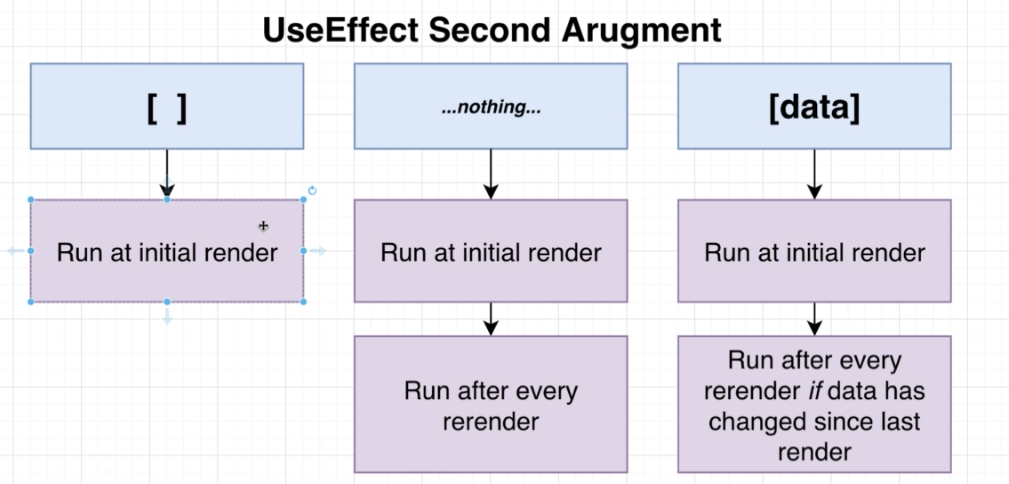
useEffect 的 callback function不能放 async function,要寫成以下幾種:
// 方法1 - 影片的建議寫法
useEffect(() => {
const search = async () => {
await axios.get('...')
}
search()
}, [term])
// 方法2 - 立即函式
useEffect(() => {
(async () => {
await axios.get('...')
})()
}, [term])
// 方法3 - Promise
useEffect(() => {
axios.get('...')
.then((response) => {
}
}, [term])
字串轉為 html的方式(因有XSS攻擊風險所以property命名上特別提醒)
<span dangerouslySetInnerHTML={{ __html: result.snippet }} />
164~168 講的好像比較像 debounce 不是 throttle。影片教學用 useEffect自己刻throttle(雖然我覺得是debounce)蠻有趣的
useEffect 中return callback function為 clean up function,會在下一次執行之前被調用
170 影片講者說為較進階議題可跳過。
如果在 useEffect 當中使用監聽對象以外的 state 或 prop,會跑出 warning告知需要將該變數加入監聽。

確實是有點複雜,雖然是看的懂,但不曉得有什麼其他的情況可以套用同樣的概念?以我的理解,react希望 useEffect的callback function不要依賴其他的狀態的原因是要避免 side effect,而講者提出來的解法是令外增加一個狀態,並額外增加一個 useEffect來監聽這個新的狀態,這樣就可以不需要依賴原先所依賴的外部狀態(看程式上確實是如此,但我也不曉得該如何解譯原理?)
用 hooks實作Controlled Element(同Vue雙向綁定)範例
// 外層
export default () => {
const [selected, setSelected] = useState(options[0])
return (
<div>
<Dropdown
selected={selected}
onSelectedChange={setSelected}
options={options}
/>
</div>
)
}
// Dropdown
const Dropdown = ({ options, selected, onSelectedChange }) => {
const renderOptions = options.map((option) => {
return (
<div
key={option.value}
className="item"
onClick={() => onSelectedChange(option)}
>
{option.label}
</div>
)
})
return (
// 略
)
}
在 JSX 當中 null代表不會渲染任何東西,所以如果用map函式中要篩選掉某一項可以 return null(不過我覺得在組JSX前先用filter做好篩選應該是比較好的做法)
下拉選單點擊外面要關起來,影片的做法是在 html的 body中加入 eventListener捕捉 bubble up傳來的事件
useEffect(() => {
document.body.addEventListener('click', () => {
setOpen(false)
})
}, []);
影片(182)說明 body上新增的監聽事件會第一個被執行,但是我聽不懂為什麼順序是這樣?
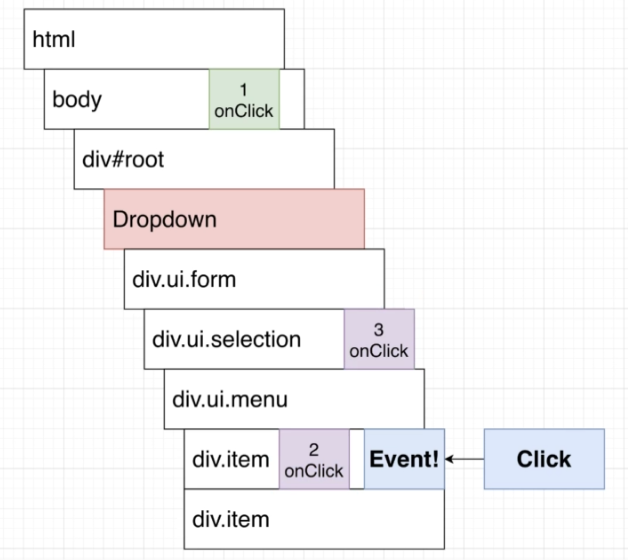
解法是「在事件中判斷點擊的 dom是 Dropdown當中的 dom還是以外的 dom」
const ref = useRef()
useEffect(() => {
document.body.addEventListener('click', () => {
if (ref.current.contains(event.target)) {
return
}
setOpen(false)
})
}, []);
return (
<div ref={ref}>
略
)
順便筆記英文單字
程式相關
scaffold 腳手架/鷹架
ternary expression 三元運算子
template string 樣板字符,或稱 backtick 重音符號 → ``
apostrophe 撇號,或稱 single quate 單引號 → '
destructure, destructure out 解構
parenthess 括號
invoke 調用 e.g. Callback gets invoked
plain text 純文本
口語/一般單字
put on 放上
very top of the page 頁面最上方
quick pause 短暫休息一下
flip back, flip back over 翻回來
determine 決定
decline 拒絕
perspective 看法
usable 可用的
straightforward 直接了當
attempt 試圖
frequently 頻繁
hemisphere 半球
ultimate 最終的
repetitive 重複的
10 pixels away from... 離... 10px
this css file gets linked up to our project
by default
indicate 表明
elegant 優雅的
deceptively 欺騙性的
tremendous number of 大量的
wrap up, a quick wrap up 快速總結
tackle 處理、對付
convention 慣例、傳統
in particular 特別是、尤其是
precisely 明確地
segment 段、一小部份
settle 定居、解決、安排 e.g. we're goring to settle on one option 我們將會決定一個選項
singular 單數、單個(強調特定的一個)
distinct 清楚的
laid out 佈置
scrunch, scrunch down 壓縮(排版上)
adjust 調整
underneath 下面
we'll be all set 我們要完成了
tile 磁磚
consistent 持續的
misleading 誤導